Port Forwarding
Port forwarding (PF) is a layer 3 forwarding service based on vRouters
or VPC vRouters. It can forward the port traffics of specified public IP addresses to
the ports of corresponding VM IP addresses. If your public IP addresses are
insufficient, port forwarding can provide multiple external services for VM instances to
save public IP resources.
- In private networks that enable the source network address translation (SNAT) service, VM instances can access the external network, but cannot be accessed by the external network. A port forwarding rule can be used to allow the external network to access some specified ports of VM instances behind SNAT.
- An elastic port forwarding rule can be dynamically attached to or detached from VM instances.
- The port forwarding service can only be provided by vRouters or VPC vRouters.
- A port forwarding rule can be created between public networks of a
vRouter or VPC vRouter and private networks of VM instances, as shown in
Port
Forwarding.
Figure 1. Port Forwarding 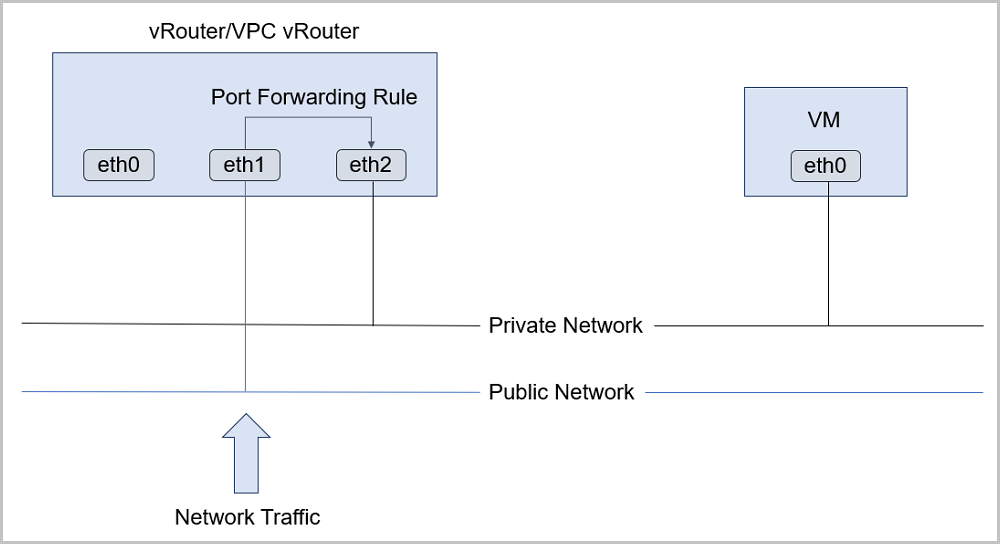
- A port forwarding rule can be created between public networks of a
vRouter or VPC vRouter and private networks of VM instances, as shown in
Port
Forwarding.
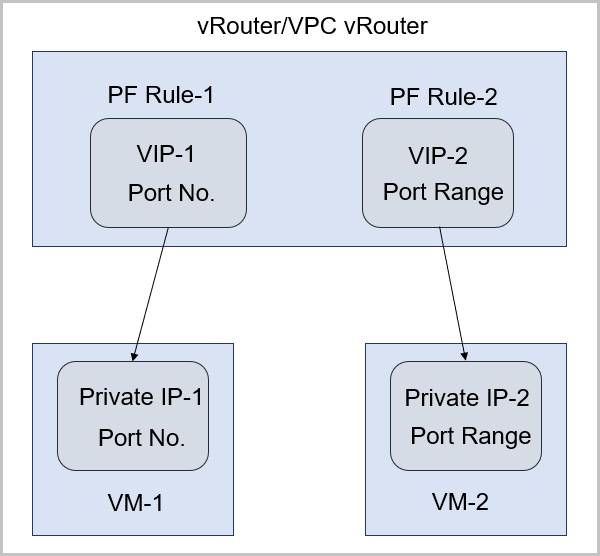
- The port forwarding service is provided by VIP.
- A VIP corresponds to an available IP address in a public IP resource pool.
- To create port forwarding by using a VIP, either create a new VIP or use an existing VIP.
- To specify port mappings for port forwarding, choose one-to-one port mapping or range-to-range port mapping, as shown in VIP - Port Forwarding.
-
Figure 2. VIP - Port Forwarding