What is Affinity Group?
An affinity group is an orchestration policy for IaaS resources to ensure the high performance and high availability of businesses...
Affinity Group Policy
ZStack Cloud provides two affinity group
policies to better manage VM instances and hosts:
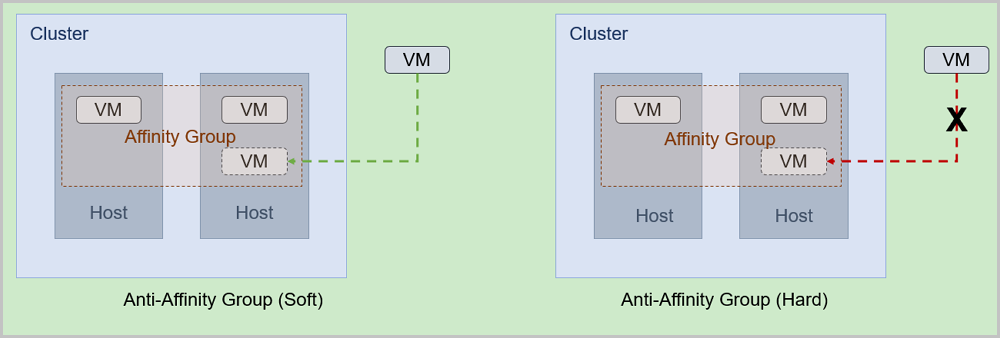
- Anti-affinity group (soft):
Allocates VM instances in the affinity group to different hosts as much as possible. If no more hosts are available, the VM instances will be allocated randomly.
- Anti-affinity group (hard):
Strictly allocates VM instances in the affinity group to different hosts. If no more hosts are available, the allocation fails.
Scenarios
This section provides some usage examples of anti-affinity group (soft) and anti-affinity group (hard) policies.
- Anti-affinity group (soft):You might want to deploy Hadoop nodes with different roles on different hosts to improve the overall system performance.
- For example, when you deploy a Hadoop system, you might find it difficult to calculate the exact number of nodes of different roles such as NameNode, DataNode, JobTracker, and TaskTracker. However, deploying nodes on different hosts is more effective. With the anti-affinity group (soft) policy, you can deploy Hadoop clusters on different hosts as much as possible. This relieves the I/O pressure and improves the overall performance of the system.
- Anti-affinity group (hard):You might want to deploy two VM instances that run an active and a standby database on different hosts to ensure high availability.
- For example, you deploy two VM instances to run an active and a standby MySQL database respectively, which cannot be down at the same time. In this case, you must deploy these two VM instances on different hosts. Due to deployment automation, you might not predict which hosts have sufficient resources. With the anti-affinity group (hard) policy, you can choose two different hosts to run these two VM instances respectively, which ensures the high availability.