What is Port Forwarding?
Port forwarding functions based on the layer-3 forwarding service of VPC vRouters. This service forwards traffic flows of the specified IP addresses and ports in a public network to specified ports of VM instances by using the specified protocol. If your public IP addresses are insufficient, you can configure port forwarding for multiple VM instances by using one public IP address and port.
- VM instances in a private network for which SNAT is enabled can access external networks. However, the VM instances in the private network are inaccessible to external networks. You can use a port forwarding rule to allow access to specified ports of the VM instances from external networks.
- You can associate a port forwarding rule with a VM NIC and disassociate a port forwarding rule from a VM NIC based on your business needs.
- Port forwarding services are provided only by VPC vRouters.Port forwarding rules are applied to a public network associated with a VPC vRouter and a private network where VM instances reside, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 1. Port Forwarding 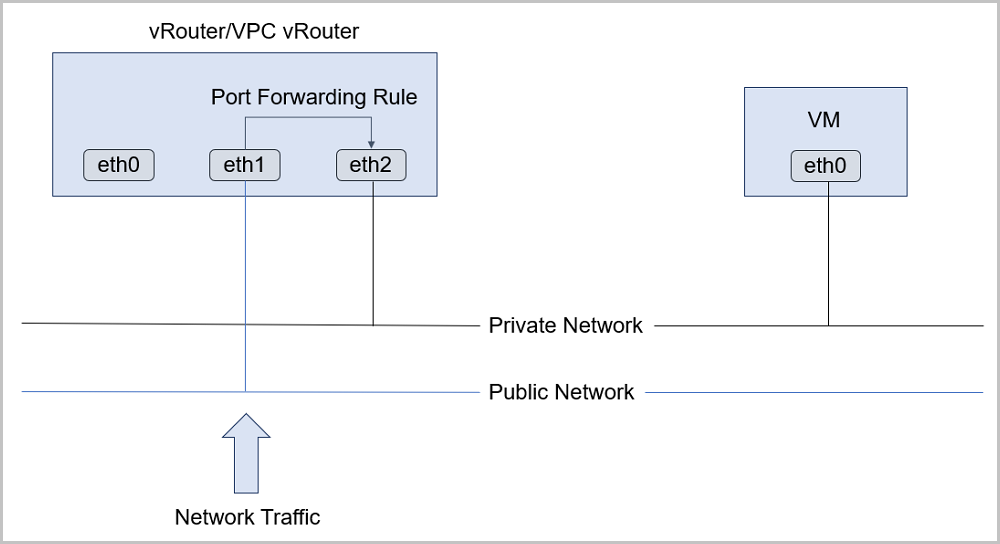
- Port forwarding is achieved by using a virtual IP address (VIP).
- A VIP is an available IP address in a public network.
- You can use an existing VIP or create a VIP to provide port forwarding services.
- Two port forwarding methods are supported: port-to-port mapping and port range-based mapping.
Figure 2. VIP-Port Forwarding 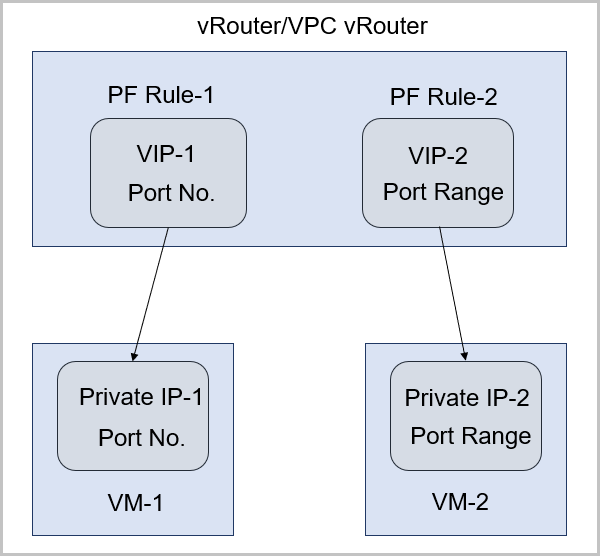
Limits
The port forwarding service has the following limits:
- The firewall policy of a VM instance must open the port specified for port forwarding.
- The ports used for port forwarding by the same VIP must be unique.
- You can use a VIP to provide port forwarding services for different ports of multiple VM NICs in the same L3 network.
- You can use only one VIP to provide port forwarding services for a VM instance.
- If you disassociate a VIP from a VM instance and then associate the VIP with a VM instance, you can select VM NICs that reside in the same L3 network as the previously disassociated VM instance.
- The source port range and target port range used for port forwarding must be consistent. For example, if you set the source port range to 22-80, the target port range must also be 22-80.