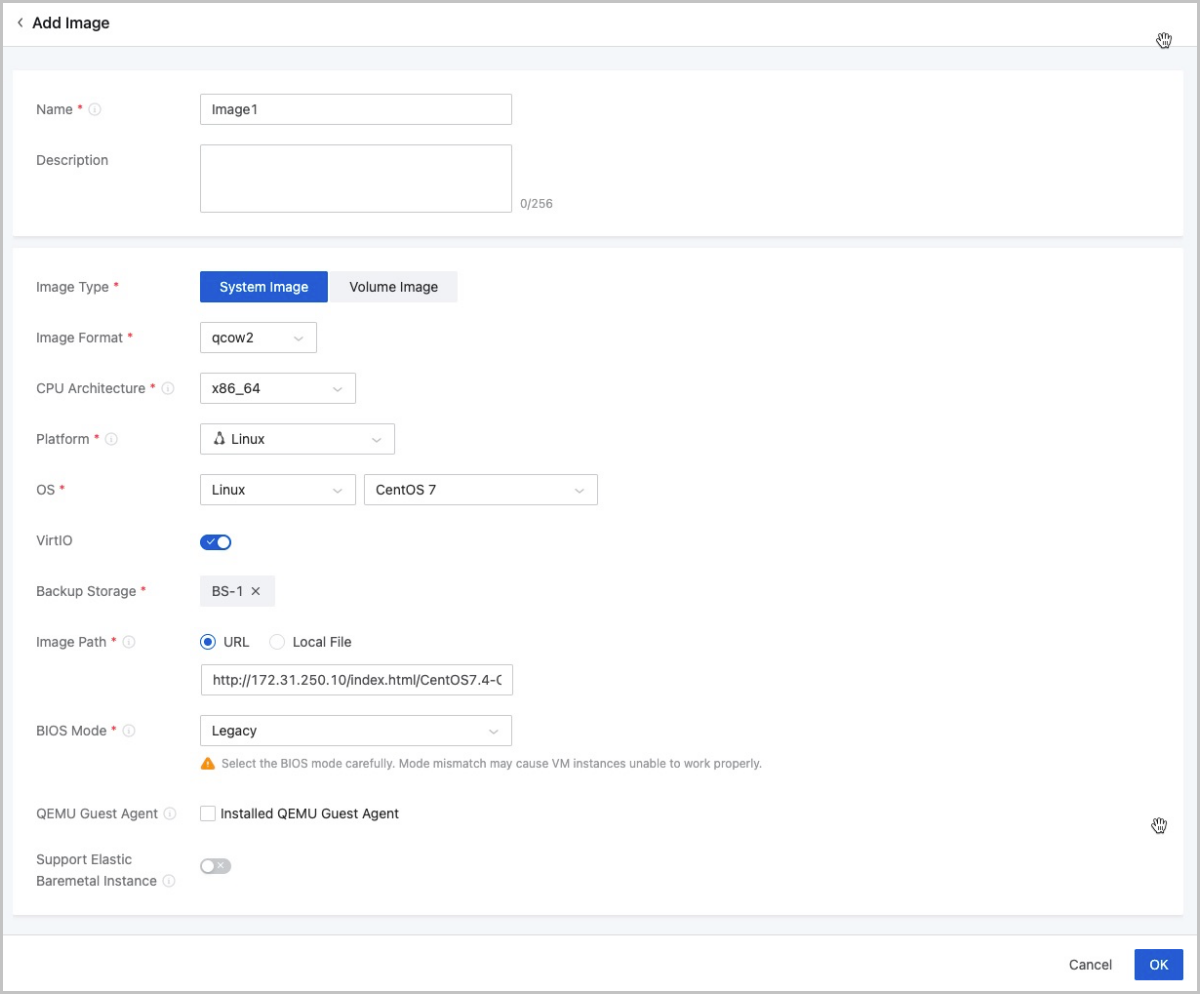
Add an Image
On the main menu of ZStack Cloud, choose . On the Image page, click Add Image. The Add Image page appears.
The following lists the two image addition scenarios:
- Add a system image
- Add a volume image
Add System Image
On the displayed page, set the following parameters:
- Name: Enter a name for the image.
The name must be 1 to 128 characters in length and can contain Chinese characters, English letters, digits, hyphens (-), underscores (_), periods (.), parenthesis (), colons (:), and plus signs (+).
- Description: Optional. Enter a description for the image.
- Image Type: System Image.
- Image Format: Select an image format. You can select qcow2, iso, or raw.
- CPU Architecture: Select a CPU architecture for the
image. VM instances created from the image use this CPU
architecture.
 Note: If you select aarch64 or mips64, set the BIOS mode to
UEFI.
Note: If you select aarch64 or mips64, set the BIOS mode to
UEFI. - Platform: Select an image platform type.The platform type of an image decides whether the VM instance created based on the image uses KVM VirtIO drivers, including VirtIO disk drivers and VirtIO NIC drivers. The following lists the available platform types of an image:
- Linux: uses VirtIO drivers.
- Windows: does not use VirtIO drivers. QEMU is used to emulate devices. The operating system (OS) contained in the image is Windows that does not install VirtIO.
- WindowsVirtio: uses VirtIO drivers. The operating system (OS) contained in the image is Windows that has installed VirtIO drivers, including VirtIO disk drivers and VirtIO NIC drivers.
- Other: does not use VirtIO drivers. QEMU is used to emulate devices. The operating system (OS) contained in the image can be of any type and version. This platform type allows compatibility with earlier versions of an OS that does not support VirtIO drivers, such as RHEL 5.8.
- Paravirtualization: uses VirtIO drivers. The operating system (OS) contained in the image can be of any type and version that has installed VirtIO drivers.
- OS: Select an operating system that is consistent with the image.
- VirtIO: Choose whether to enable VirtIO according to your actual operating system and platform.
- Backup Storage: Select a backup storage.
- Image Path: Specify an image URL or upload a local
file:
- URL: Enter a specified URL to add an image.
You can enter a URL by using either of the following syntax:
- A URL that starts with http or https:
- Syntax: http://host[:port]/path/file or https://host[:port]/path/file.
- A URL that starts with ftp:
- Syntax that does not specifies the user: ftp://hostname[:port]/path/file.
- Syntax that specifies the user: ftp://user:password@hostname[:port]/path/file.
- A URL that starts with sftp:
- Syntax that specifies the user identity: sftp://user:password@hostname[:port]/path/file
- User-identity-free syntax: sftp://user@hostname[:port]/path/file.
- The absolute path of an image file that is stored on a
backup storage. The backup storage that stores the image
file can be an ImageStore backup storage.
Syntax: file:///path/file
 Note:
Note:
- The image file to be added to the destination backup storage must exist and the backup storage needs to have access to the URL of the image file.
- If you enter a URL that starts with sftp and does not specify user identity, make sure that you enable password-free SSH login to the server that stores the image file.
- For the progress bar and resumption from breakpoint
features:
- If you use an ImageStore backup storage, a progress bar will appear to display the upload progress. In addition, upload resumption from breakpoints is also supported.
- If you use a Ceph backup storage, a progress bar will appear to display the upload progress. However, upload resumption from breakpoints is not supported.
- If you specify a URL with the
file:/// syntax to add an
image:
- Ceph backup storage does not support the file:/// syntax.
- The three forward slashes (/) in file:/// represents the absolute path of a file on a backup storage. For example, if you specify the URL file:///opt/dvd/image-1.4.qcow2, you add the image file named image-1.4.qcow2 in the /opt/dvd path of a backup storage to the Cloud.
- A URL that starts with http or https:
- Local File: Select a local image file that
the current browser can access and upload the image file to the
specified backup storage. The backup storage that stores the image
file can be an ImageStore or Ceph backup storage.
 Note: If you upload a local image file, the
local browser serves as a transfer station. Do not refresh or
close the browser or stop management node services. Otherwise,
the image addition may fail.
Note: If you upload a local image file, the
local browser serves as a transfer station. Do not refresh or
close the browser or stop management node services. Otherwise,
the image addition may fail.
- URL: Enter a specified URL to add an image.
You can enter a URL by using either of the following syntax:
- BIOS Mode: Select a BIOS mode.
You can select the Legacy or UEFI mode.
- Legacy: This mode supports all operating systems (OSs) and ensures stable operation. We recommend you select this mode.
- UEFI: This mode supports Windows and CentOS. Note that the Compatibility Support Module (CSM) must be enabled for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2.
 Note: Mode mismatch may cause VM instances unable
to work as expected. Select a mode based on your business needs:
Note: Mode mismatch may cause VM instances unable
to work as expected. Select a mode based on your business needs:- If you add an image in qcow2 or raw format, select the mode consistent with the mode used when the image was created.
- If you add an image in iso format, you can select either of the two modes. OS will be boot based on the selected mode.
- If you want to boot the OS of a VM instance in UEFI mode, we
recommend that you select a VM image that is created from one of
the OS listed in the following table.
OS BIOS Mode Supported Versions Windows UEFI - Windows 8 or later
UEFI with CSM - Windows 7
- Windows Server 2008 R2
Linux UEFI - CentOS 7.2
- CentOS 7.3
- CentOS 7.4 or later
- As mentioned in the preceding table, you can
create a Linux-based VM instance by using an image that is
created from CentOS 7.4 or later and that uses the UEFI mode.
However, if the VM instance is restarted, the system may enter
the UEFI Shell. To avoid this situation, you can use one of the
following methods to boot the OS:
- Use a script to skip the UEFI Shell and directly load
the OS.In the installed OS, run the
vim /boot/efi/startup.nshcommand to create a file, enter the following content in the file, and save the file. Then when you restart the VM instance, the UEFI Shell is skipped and the OS is boot.FS0: CD EFI CD centos shimx64-centos.efi - Manually exit the UEFI Shell.If you have entered the UEFI Shell, run the following commands to exit the UEFI Shell:
Shell> fs0: FS0:\> cd EFI FS0:\EFI\> cd centos FS0:\EFI\centos\> shimx64-centos.efi
- Use a script to skip the UEFI Shell and directly load
the OS.
- If you use a Window-based VM instance such
as Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, or Windows 10
that has its OS boot in UEFI mode, the following figure will
display after you start the VM instance. In this case, press any
key to continue the installation of the OS. Otherwise, the
system will enter the UEFI Shell.If you have entered the UEFI Shell, run the following commands to exit the UEFI Shell:
Figure 1. Press Any Key to Continue 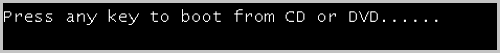
Then press any key in a timely manner. Otherwise, the system will reenter the UEFI Shell.Shell> fs0: FS0:\> dir FS0:\> cd EFI FS0:\EFI\> cd BOOT FS0:\EFI\BOOT\> BOOTX64.EFI
- Enable CSM: Optional. Choose whether to use the
CSM.
The CSM can only be used for devices that can only work in Legacy mode and OSs that do not support or partially support the UEFI mode.
 Note: For Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, you must enable
the CSM.
Note: For Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, you must enable
the CSM. - QEMU Guest Agent: Optional. Choose whether the
current image has installed QEMU Guest Agent (QGA).
 Note: If the image has
installed QGA and has set the agent as auto-start and you use the image
to create a VM instance, you can modify the passwords of this VM
instance, the clones of this VM instance, and the VM instances created
from the image that is created from this VM instance when all these
instances are in running state.
Note: If the image has
installed QGA and has set the agent as auto-start and you use the image
to create a VM instance, you can modify the passwords of this VM
instance, the clones of this VM instance, and the VM instances created
from the image that is created from this VM instance when all these
instances are in running state. - Support Elastic Baremetal Instance:
Optional. Choose whether the image can be used to create an elastic
baremetal instance. If enabled, the image can be used to create an elastic
baremetal instance.
 Note: When you add an image of an elastic baremetal
instance, make sure:
Note: When you add an image of an elastic baremetal
instance, make sure:- The image has installed the agent. Otherwise, after you use the image to create an elastic baremetal instance, you cannot open the console or modify the password of the elastic baremetal instance. In addition, you cannot attach a volume or network to the instance or detach a volume or network from the instance.
- The BIOS mode of the image is the same the system configuration. Default: UEFI. If you want to use Legacy, contact the technical support.
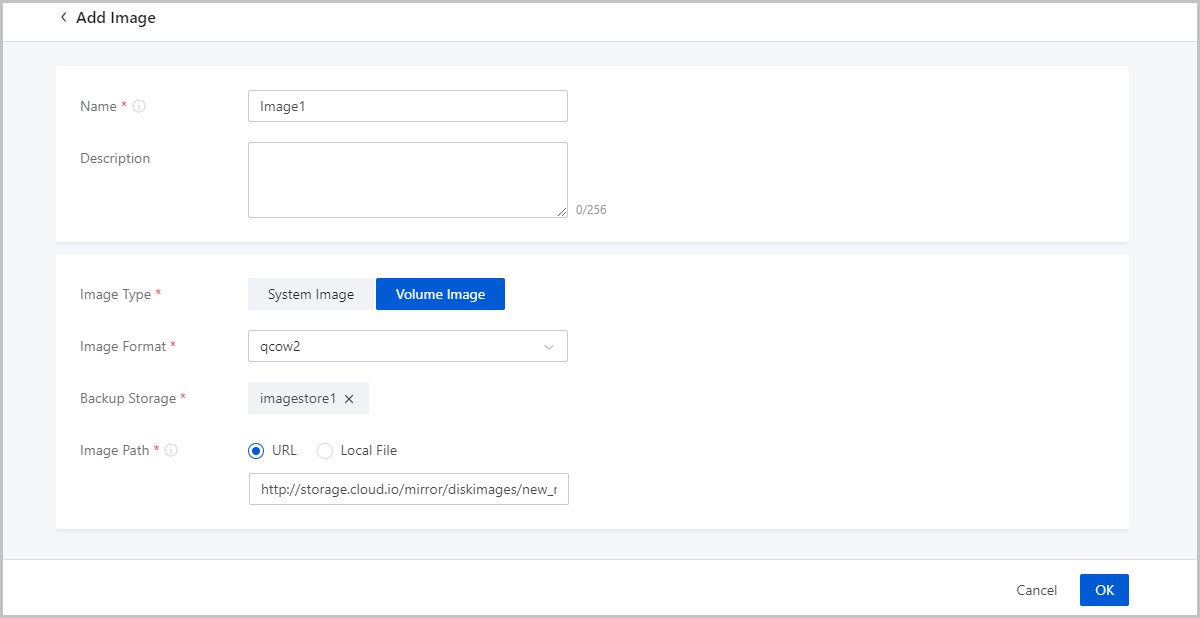
Add Volume Image
On the displayed page, set the following parameters:
- Name: Enter a name for the image.
- Description: Optional. Enter a description for the image.
- Image Type: Select System Image.
- Image Format: Select an image format. You can select qcow2, iso, or raw.
- Backup Storage: Select a backup storage.
- Image Path: Specify an image URL or upload a local file.